Pubic Lice
What are pubic lice (crabs)?
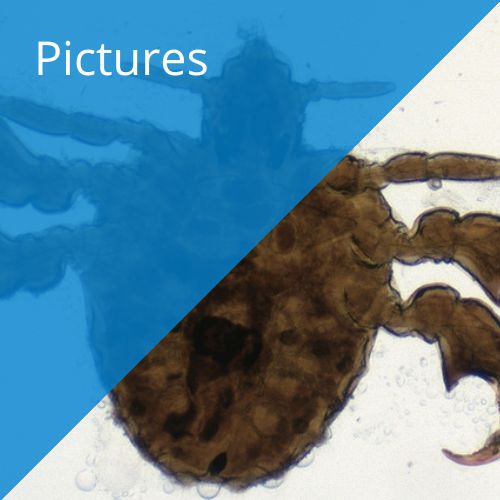
The crab louse (Pthirus pubis) is smaller than the head louse, 1–2 mm long, and has a rounder body. It resembles a small crab. Its powerful hind legs have large claws. These claws are too wide to grip ordinary hair, but are ideal for gripping the coarse hair of the pubic region and armpits. Flat lice may also be found on eyelashes, eyebrows, armpits and in beards. The life cycle of the pubic louse is about 25 days. The eggs hatch after one week. The female lays about 25 eggs during her lifetime. The eggs are attached to the hairs next to the skin.
This skin parasite lives on human blood and thrives best on moist, warm skin surfaces. Without access to blood, pubic lice die within 24 hours. Itching is the most common symptoms of pubic louse infestation. The intense itch results from pubic lice sucking blood. Pubic louse infestation is not dangerous, but results in intense itching and is highly contagious. The intense itching on irritated skin surfaces may result in sores that can become infected.
How do Pubic lice (crabs) spread?
No official statistics are available on how many people suffer from pubic lice every year in Sweden, but this problem has shown an upward trend in recent years. Pubic lice infestation is often associated with poor hygiene, but this is incorrect. Anyone can be afflicted with pubic lice and infection is not related to personal hygiene. There is no effective way to prevent an infection. Pubic lice have also been associated with a promiscuous lifestyle, which makes it difficult to discuss openly. It is important to notify any potentially affected individuals to minimize the risk of spreading pubic lice.
Pubic lice are mainly spread through close bodily contact, such as intercourse. Pubic lice can also be spread via bedding and towels, as well as improperly cleaned tanning booths. The areas most prone to infestation include pubic hair, arm hair, beards and chest hair. In cases where children are infected by pubic lice, they tend to be found in eyebrows and eyelashes. Eyebrows and eyelashes are rarely involved in adults. In cases where adults are afflicted in these areas, it is usually the result of oral sex.
If pubic lice are found in the eyebrows or eyelashes, a doctor should be contacted before taking measures to ensure the right treatment. The same applies to pregnant women who need to be treated for pubic lice.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is important to wash bedding, towels and clothing, preferably at 60o C to minimize the risk of spreading. Textiles and objects that are difficult to wash may instead be sealed and stored for one month to ensure that all pubic lice are dead.
Page last edited 2025-10-28
Treatment information
Tenutex® is a cutaneous emulsion containing benzyl benzoate / disulfiram. Tenutex® is a prescription free medicine that is active against Scabies, Head lice, and Pubic lice. Ask your doctor or nurse before using Tenutex® for treating Pubic lice or Scabies. Treatment of Scabies: Wash and dry your body. Carefully massage the hole body except your head with Tenutex®. Only in infants should the head be treated. Wash off thoroughly after 24 hours. In severe infections, repeat the treatment after 1 week. Avoid contact with the eyes. Tenutex® contains cetostearyl alcohol which may cause local skin reactions (e.g. contact dermatitis). Read the patient information leaflet carefully before use.