Symptoms
How can we tell if we are infected by pubic lice (crabs)?
The main symptom of pubic lice infestation is annoying itching. It takes about one month from the time of infection for pubic lice to mature and begin to cause an annoying itch by biting the skin. The itching is usually more intense at night and may cause sleeping problems.
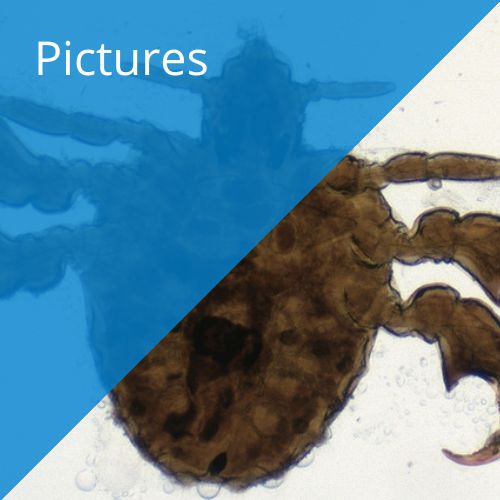
Pubic lice are well camouflaged and because they are so small they are difficult to detect. After a blood meal they swell and become dark red. Louse feces result in a reddish brown powder, which sometimes can be detected on skin or underwear. In cases of heavy infestation, bluish round spots may be seen on the trunk and thighs, the result of pubic louse bites.
It is important to avoid intense scratching of the affected skin areas since the bites in combination with intense scratching may lead to infected sores. To relieve itching, the affected area of the skin may be treated with a hydrocortisone cream, available at the pharmacy without a prescription. It is common for itching to continue after treatment. Generally this does not mean that the treatment was unsuccessful, but rather that the hypersensitivity reaction to the pubic lice is still ongoing in the skin.
Pubic lice are almost always spread through direct contact or between people sharing the same bed. To minimize the risk of contagion it is important to openly discuss pubic lice and inform exposed partners that may have become infected.
Sidan uppdaterades 2025-10-28
Treatment information
Tenutex® is a cutaneous emulsion containing benzyl benzoate / disulfiram. Tenutex® is a prescription free medicine that is active against Scabies, Head lice, and Pubic lice. Ask your doctor or nurse before using Tenutex® for treating Pubic lice or Scabies. Treatment of Scabies: Wash and dry your body. Carefully massage the hole body except your head with Tenutex®. Only in infants should the head be treated. Wash off thoroughly after 24 hours. In severe infections, repeat the treatment after 1 week. Avoid contact with the eyes. Tenutex® contains cetostearyl alcohol which may cause local skin reactions (e.g. contact dermatitis). Read the patient information leaflet carefully before use.